“The operation confirmed that our armed forces are prepared,” Iranian president Ebrahim Raisi informed crowds gathered Wednesday in Tehran to mark Military Day. Parades within the Iranian capital featured most of the identical munitions used within the assault on Israel.

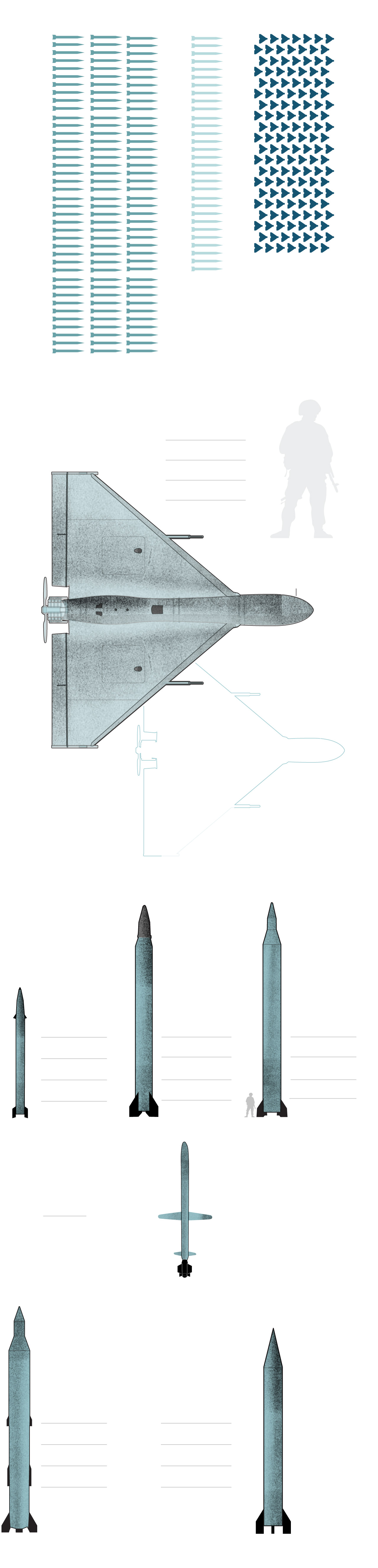
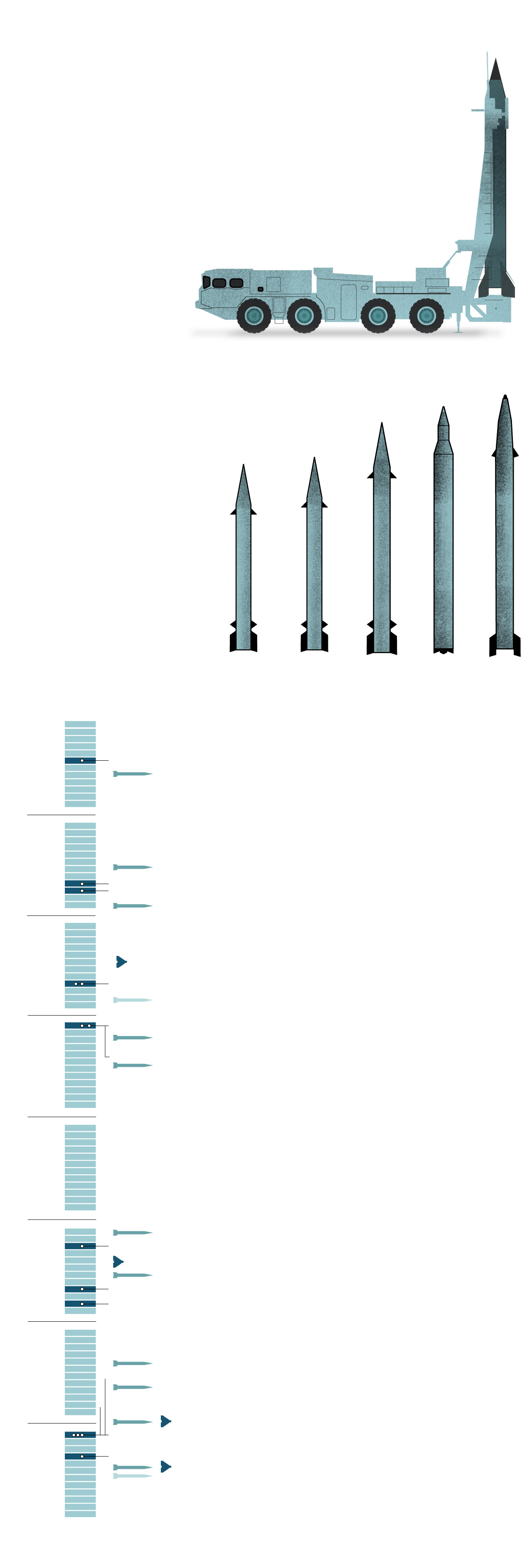
What Iran used towards Israel
These drones can ship small payloads of explosives in self-detonating assaults.
Max. take off weight: 440 lb.
Vary: About 1,100 – 1,500 miles
Its nostril incorporates a warhead and might be geared up with a digicam.
Max. take off weight: 300 lb.
The Shahed-131 is an earlier model of Shahed-136 with an identical precept of operation. The format and aerodynamics are additionally an identical.
The Kheibar Shekan MRBM is a solid-propellant ballistic missile designed by the IRGC.
Warhead weight: 1,100 lb.
The Emad MRBM is an Iranian-designed, liquid-fuel ballistic missile primarily based on Shahab-3.
Warhead weight: 1,650 lb.
The Ghadr-1 MRBM appears to be an improved variant of the Shahab-3A. Additionally it is known as the Ghadr-101 and the Ghadr-110.
Warhead weight: 1,760 lb.
The Sejjil-1 Iranian MRBM is a two-stage, solid-propellant, surface-to-surface missile.
Warhead weight: 1,540 lb.
The Shahab-3 is a MRBM developed by Iran and primarily based on the North Korean Nodong-1.
Warhead: Single or a number of
with 5 warheads of 617 lb.
Sources: OE Information Integration Community (ODIN),
CSIS Missile Protection Mission

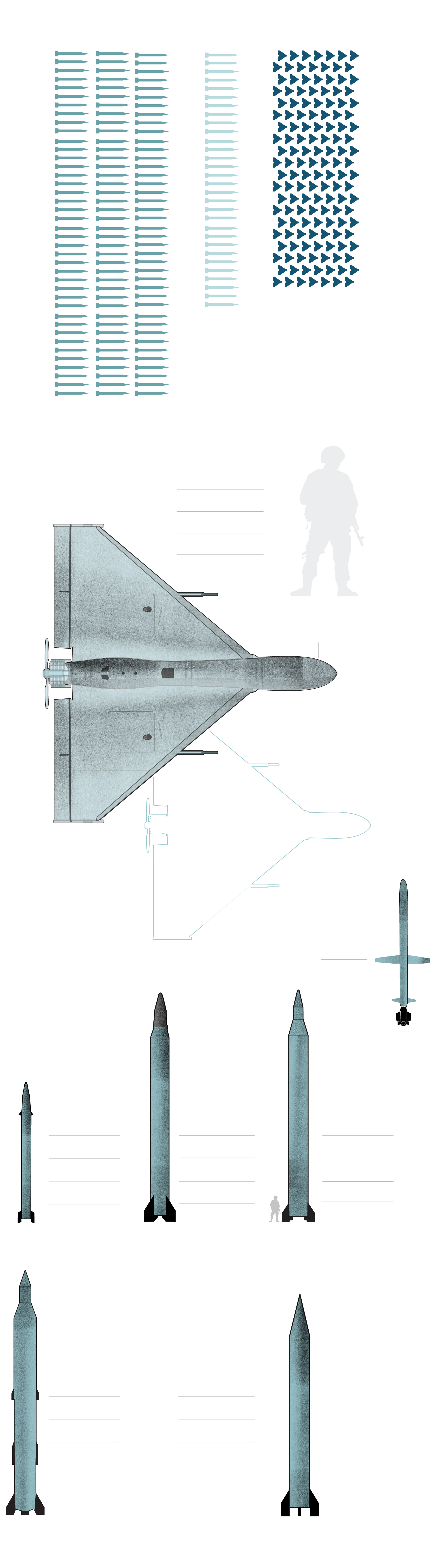
What Iran used towards Israel
These drones can ship small payloads of explosives in self-detonating assaults.
Max. take off weight: 440 lb.
Vary: About 1,100 – 1,500 miles
Its nostril incorporates a warhead and might be geared up with a digicam.
Max. take off weight: 300 lb.
The Shahed-131 is an earlier model of Shahed-136 with an identical precept of operation. The format and aerodynamics are additionally an identical.
The Kheibar Shekan MRBM is a solid-propellant ballistic missile designed by the IRGC.
Warhead weight: 1,100 lb.
The Emad MRBM is an Iranian-designed, liquid-fuel ballistic missile primarily based on Shahab-3.
Warhead weight: 1,650 lb.
The Ghadr-1 MRBM appears to be an improved variant of the Shahab-3A. Additionally it is known as the Ghadr-101 and the Ghadr-110.
Warhead weight: 1,760 lb.
The Sejjil-1 Iranian MRBM is a two-stage, solid-propellant, surface-to-surface missile.
Warhead weight: 1,540 lb.
The Shahab-3 is a MRBM developed by Iran and primarily based on the North Korean Nodong-1.
Warhead: Single or a number of
with 5 warheads of 617 lb.
Sources: OE Information Integration Community (ODIN),
CSIS Missile Protection Mission
What Iran used towards Israel
These drones can ship small payloads of explosives in self-detonating assaults.
Max. take off weight: 440 lb.
Vary: About 1,100 – 1,500 miles
Its nostril incorporates a warhead and might be geared up with a digicam.
Max. take off weight: 300 lb.
The Shahed-131 is an earlier model of Shahed-136 with an identical precept of operation. The format and aerodynamics are additionally an identical.
The Emad MRBM is an Iranian-designed, liquid-fuel ballistic missile primarily based on Shahab-3.
The Ghadr-1 MRBM appears to be an improved variant of the Shahab-3A. Additionally it is known as the Ghadr-101 and the Ghadr-110.
The Kheibar Shekan MRBM is a solid-propellant ballistic missile designed by the IRGC.
The Sejjil-1 Iranian MRBM is a two-stage, solid-propellant, surface-to-surface missile.
The Shahab-3 is a MRBM developed by Iran and primarily based on the North Korean Nodong-1.
Warhead: Single or a number of
with 5 warheads of 617 lb.
Warhead weight: 1,540 lb.
Sources: OE Information Integration Community (ODIN), CSIS Missile Protection Mission
What Iran used towards Israel
These drones can ship small payloads of explosives in self-detonating assaults.
Max. take off weight: 440 lb.
Vary: About 1,100 – 1,500 miles
Its nostril incorporates a warhead and might be geared up with a digicam.
Max. take off weight: 300 lb.
The Shahed-131 is an earlier model of Shahed-136 with an identical precept of operation. The format and aerodynamics are additionally an identical.
The Emad MRBM is an Iranian-designed, liquid-fuel ballistic missile primarily based on Shahab-3.
The Ghadr-1 MRBM appears to be an improved variant of the Shahab-3A. Additionally it is known as the Ghadr-101 and the Ghadr-110.
The Kheibar Shekan MRBM is a solid-propellant ballistic missile designed by the IRGC.
Warhead weight: 1,760 lb.
Warhead weight: 1,650 lb.
Warhead weight: 1,100 lb.
The Sejjil-1 Iranian MRBM is a two-stage, solid-propellant, surface-to-surface missile.
The Shahab-3 is a MRBM developed by Iran and primarily based on the North Korean Nodong-1.
Warhead: Single or a number of
with 5 warheads of 617 lb.
Warhead weight: 1,540 lb.
Sources: OE Information Integration Community (ODIN), CSIS Missile Protection Mission
Raisi hailed the assault as a convincing “success,” however was additionally fast to qualify the strikes as “restricted” and “not complete.”
“If it was presupposed to be a large-scale motion, nothing would have been left of the Zionist regime,” he stated. And if Israel retaliates, Raisi pledged, “they are going to be handled fiercely and severely.”
But after analyzing the munitions utilized in Saturday’s assault and the success of regional protection programs, researchers say it’s unclear how Iran might inflict larger injury on Israel by means of standard army means.
“Iran mainly threw all the pieces it had that might attain Israel’s territory,” stated John Krzyzaniak, a researcher who research Iran’s missile packages on the Wisconsin Mission on Nuclear Arms Management. Like different analysts interviewed for this story, he has spent the previous a number of days learning launch movies, imagery of particles and interception info to determine the Iranian munitions.
His conclusion is that Tehran “used a few of each system they’ve.” And consultants stated it made sense that the Sejjil-1 and Shahab-3 missiles had been excluded from the assault.
Shahab-3 “wasn’t used as a result of it’s so previous,” stated Fabian Hinz, an Iran analyst on the Worldwide Institute for Strategic Research in Berlin. “The Sejjil is a little bit of a mysterious missile,” he stated, including that Iran has “used it very, little or no throughout maneuvers.”
Different analysts famous the Sejjil was costly to supply and will not be in manufacturing.
The amount of munitions used additionally supplies new insights into Iran’s capabilities. The deployment of over 100 ballistic missiles in a single wave means that earlier estimates that Iran has about 3,000 ballistic missiles stockpiled are most likely correct, and will even be on the low finish.
“If that is simply spherical one in all an unknown variety of rounds to return, you wouldn’t hearth a big fraction of what you might have simply within the first spherical,” Krzyzaniak stated.
The firing of over 100 ballistic missiles within the house of some minutes suggests Iran has a minimum of 100 launchers, he added — a brand new information level for researchers.
“This exhibits that Iran has actually confronted no limitation in domestically producing missiles and launchers,” he stated.
Iran’s ballistic missile arsenal, the most important of any nation within the Center East, is nearly totally homegrown. Lately Iran has demonstrated the flexibility to improve some programs, enhancing their vary and precision.
The spokesman for Iran’s armed forces, Abolfazl Shekarchi, stated the munitions used within the strikes towards Israel solely represented “a fraction of” the nation’s army’s may, in accordance with a press release revealed on state-run media.
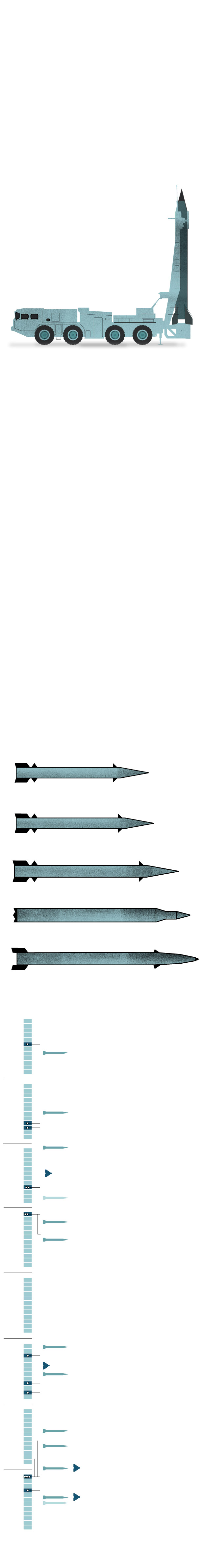
The evolution of Iran’s
missile program
Within the mid-Nineteen Eighties, Tehran acquired Scud missiles from Libya, Syria and North Korea and likewise started adapting the expertise for their very own missile variants. Through the eight-year battle with Iraq, Tehran countered primarily with Scud B missiles, which have a spread of 185 miles.
Iran developed its personal model of the Scud B, the Shahab-1, and from 1994 to 2001 fired it at bases in Iraq utilized by the opposition group Mujahedin-e Khalq.
A brand new era of missiles
After 16 years with out firing new missiles, Iran confirmed its technological advances in 2017 putting on an ISIS command heart with 6 Zolfaghars with a spread of 430 miles. In early 2024, it launched strikes towards Islamic State targets in northwest Syria utilizing Kheibar Shekan missiles that travelled 745 miles from Iran to Syria.
Kheibar Shekan, 900 miles
In opposition to Kurdish dissidents
In opposition to Oil fields and amenities
18 drones + 7 cruise missiles
15 to 22 ballistic missiles
In opposition to “Israeli strategic facilities”
At the very least 10 ballistic missiles
In opposition to Kurdish dissidents
73 launches + a minimum of 20 drones
Ballistic missiles
and suicide drones
Koya, Iraq
Sulaimaniyah,
Iraq
Israeli “spy headquarters”
120 ballistic missiles,
170 drones,
30 cruise missiles
Sources: United States Institute of Peace, CSIS, IDF
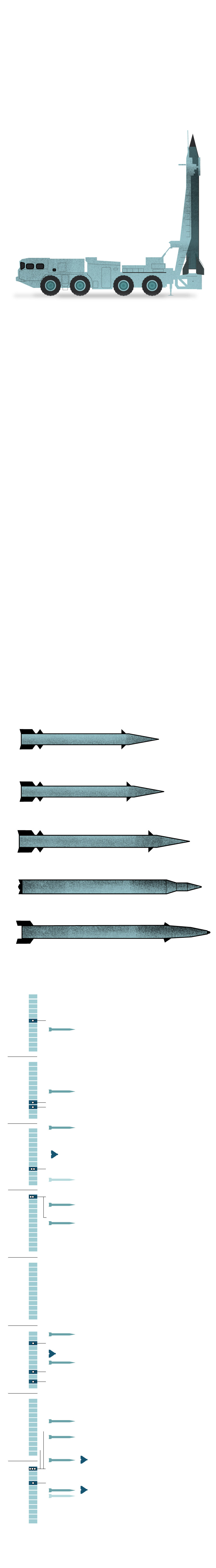
The evolution of Iran’s
missile program
Within the mid-Nineteen Eighties, Tehran acquired Scud missiles from Libya, Syria and North Korea and likewise started adapting the expertise for their very own missile variants. Through the eight-year battle with Iraq, Tehran countered primarily with Scud B missiles, which have a spread of 185 miles.
Iran developed its personal model of the Scud B, the Shahab-1, and from 1994 to 2001 fired it at bases in Iraq utilized by the opposition group Mujahedin-e Khalq.
A brand new era of missiles
After 16 years with out firing new missiles, Iran confirmed its technological advances in 2017 putting on an ISIS command heart with 6 Zolfaghars with a spread of 430 miles. In early 2024, it launched strikes towards Islamic State targets in northwest Syria utilizing Kheibar Shekan missiles that travelled 745 miles from Iran to Syria.
Kheibar Shekan, 900 miles
In opposition to Kurdish dissidents
In opposition to Oil fields and amenities
18 drones + 7 cruise missiles
15 to 22 ballistic missiles
In opposition to “Israeli strategic facilities”
At the very least 10 ballistic missiles
In opposition to Kurdish dissidents
73 launches + a minimum of 20 drones
Ballistic missiles
and suicide drones
Koya, Iraq
Sulaimaniyah,
Iraq
Israeli “spy headquarters”
120 ballistic missiles,
170 drones,
30 cruise missiles
Sources: United States Institute of Peace, CSIS, IDF
The evolution of Iran’s missile program
Iran developed its personal model of the Scud B, the Shahab-1, and from 1994 to 2001 fired it at bases in Iraq utilized by the opposition group Mujahedin-e Khalq.
Within the mid-Nineteen Eighties, Tehran acquired Scud missiles from Libya, Syria and North Korea and likewise started adapting the expertise for their very own missile variants. Through the eight-year battle with Iraq, Tehran countered primarily with Scud B missiles, which have a spread of 185 miles.
A brand new era of missiles
After 16 years with out firing new missiles, Iran confirmed its technological advances in 2017 putting on an ISIS command heart with 6 Zolfaghars with a spread of 430 miles. In early 2024, it launched strikes towards Islamic State targets in northwest Syria utilizing Kheibar Shekan missiles that travelled 745 miles from Iran to Syria.
Kheibar Shekan, 900 miles
In opposition to Kurdish dissidents
In opposition to Oil fields and amenities
18 drones + 7 cruise missiles
Qiams,
Zolfaghars and
probably
Fateh-313
15 to 22 ballistic missiles
In opposition to “Israeli strategic facilities”
At the very least 10 ballistic missiles
In opposition to Kurdish dissidents
73 launches + a minimum of 20 drones
Ballistic missiles and suicide drones
Koya, Iraq
Sulaimaniyah, Iraq
Israeli “spy headquarters”
Missiles and drones towards Jaish ul Adl
120 ballistic missiles,
170 drones, 30 cruise missiles
Sources: United States Institute of Peace, CSIS, IDF
Earlier than the assault on Israel, Iran’s most important use of ballistic missiles was in 2020, after a U.S. drone assault killed the highly effective Iranian commander Qasem Soleimani.
Iran launched greater than a dozen ballistic missiles at two U.S. army bases in Iraq, one within the nation’s west and one within the north. Whereas there have been no fatalities, dozens of U.S. service members suffered traumatic mind accidents.
Iran additionally used ballistic missiles in strikes this yr on Pakistan, Syria and Iraq.
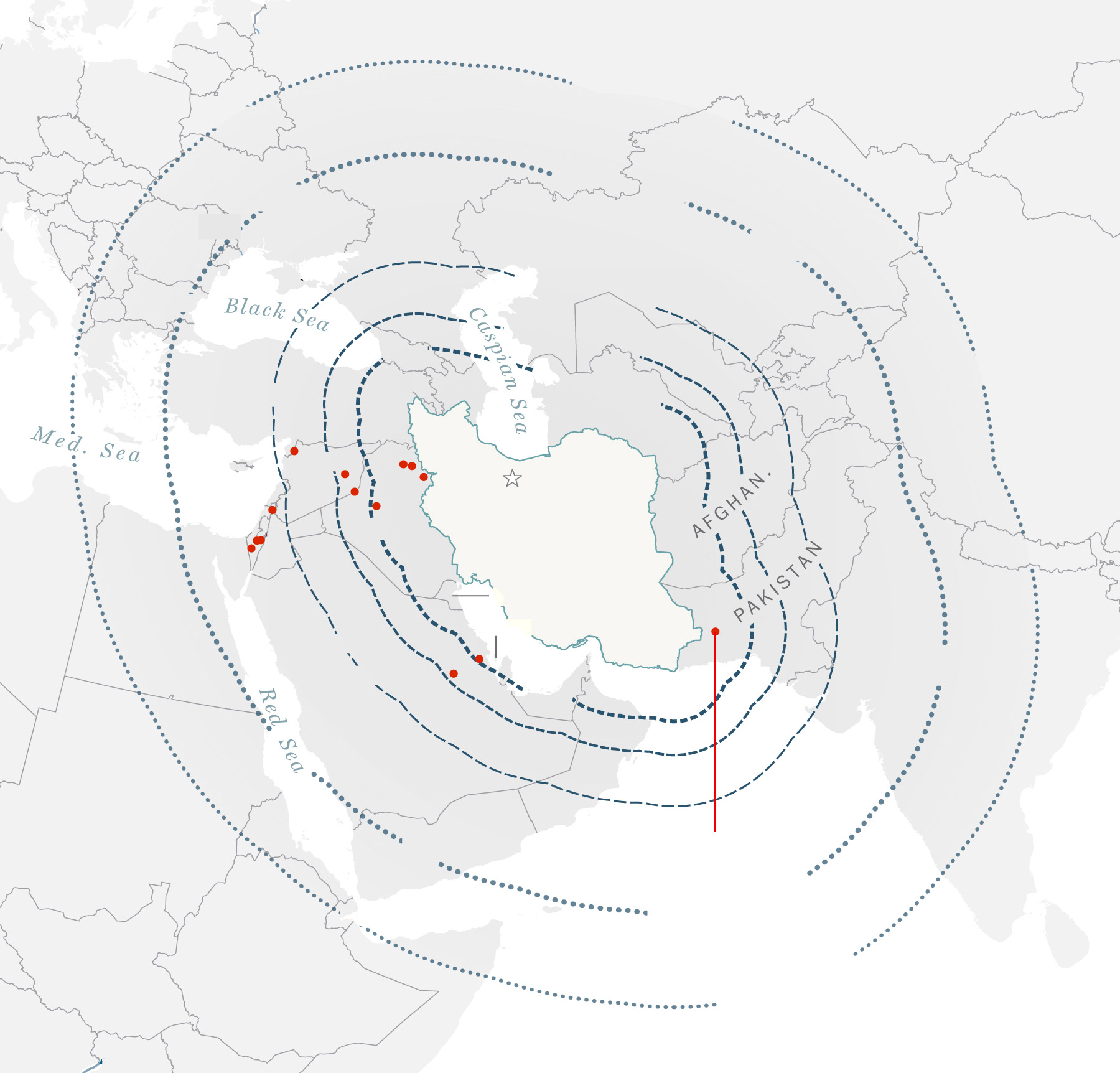
Iranian ballistic
missile ranges
Places of Iranian
missile strikes
since 2017
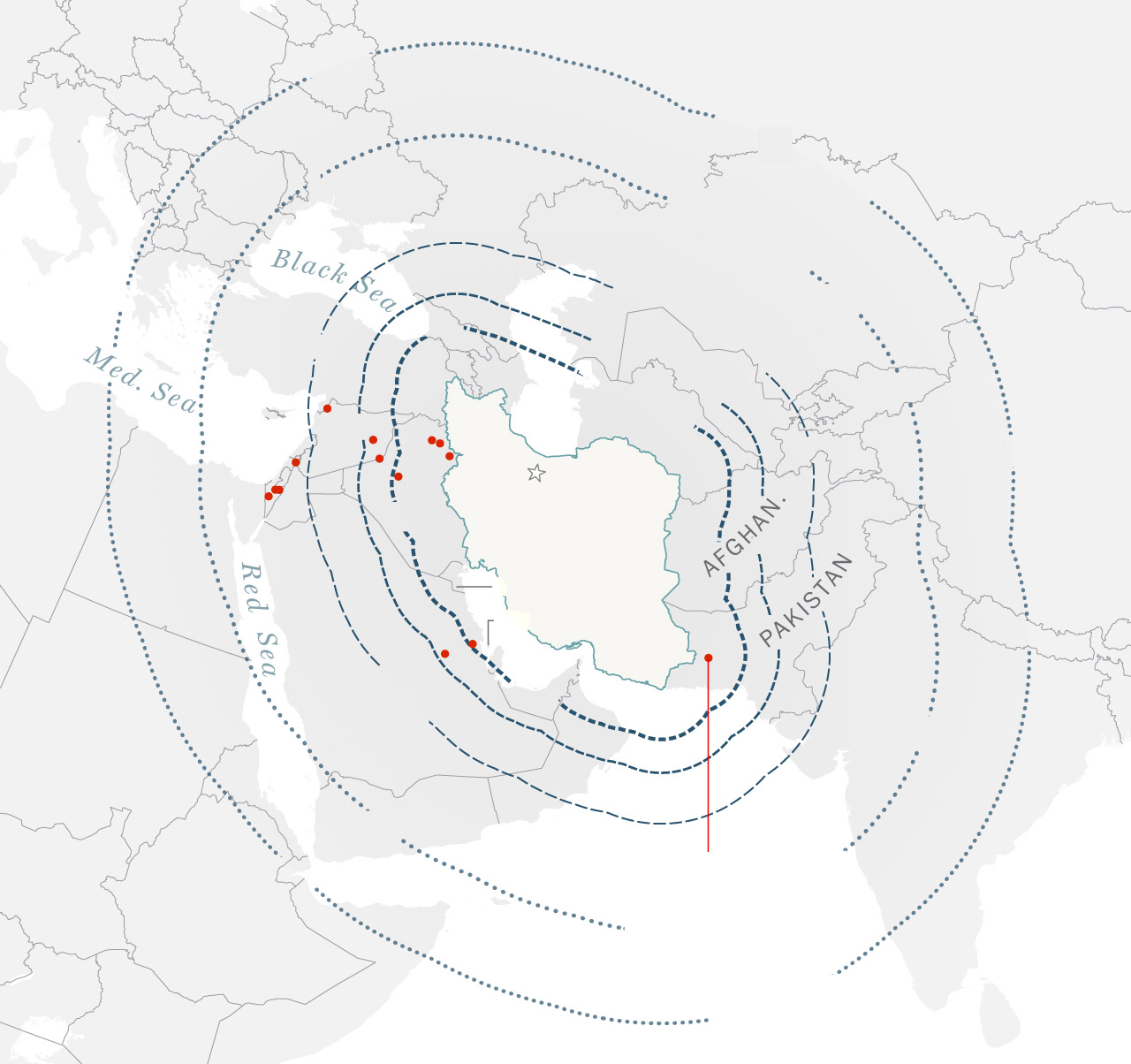
Iranian ballistic
missile ranges
Places of Iranian
missile strikes
since 2017
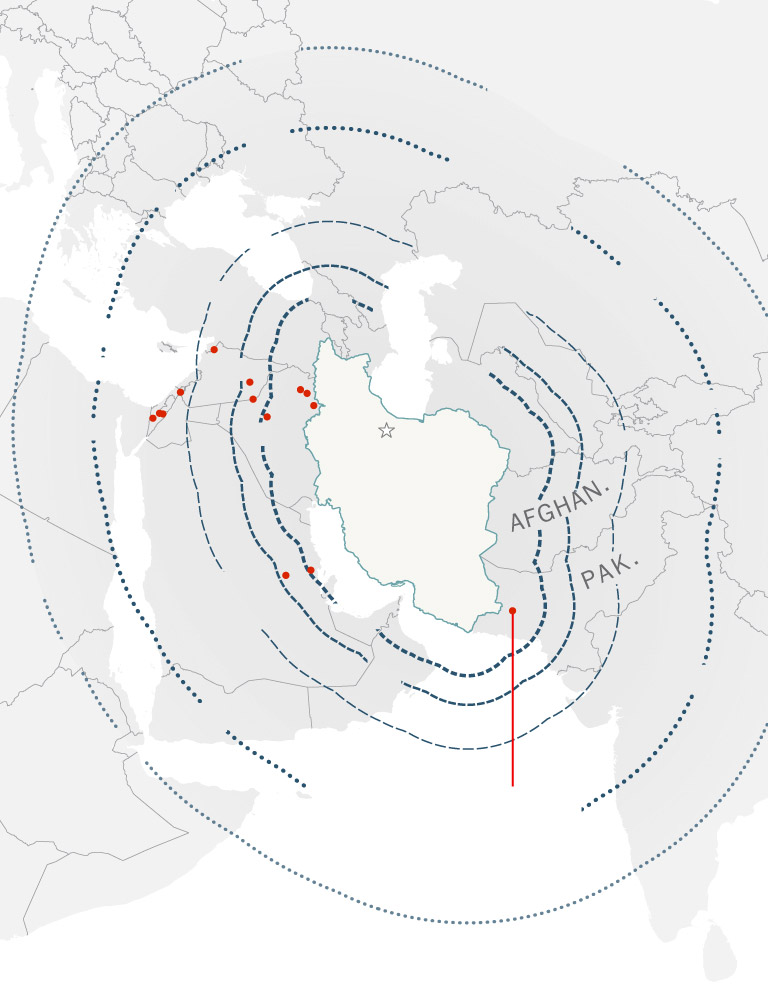
Iranian ballistic
missile ranges
Places of Iranian
missile strikes
since 2017
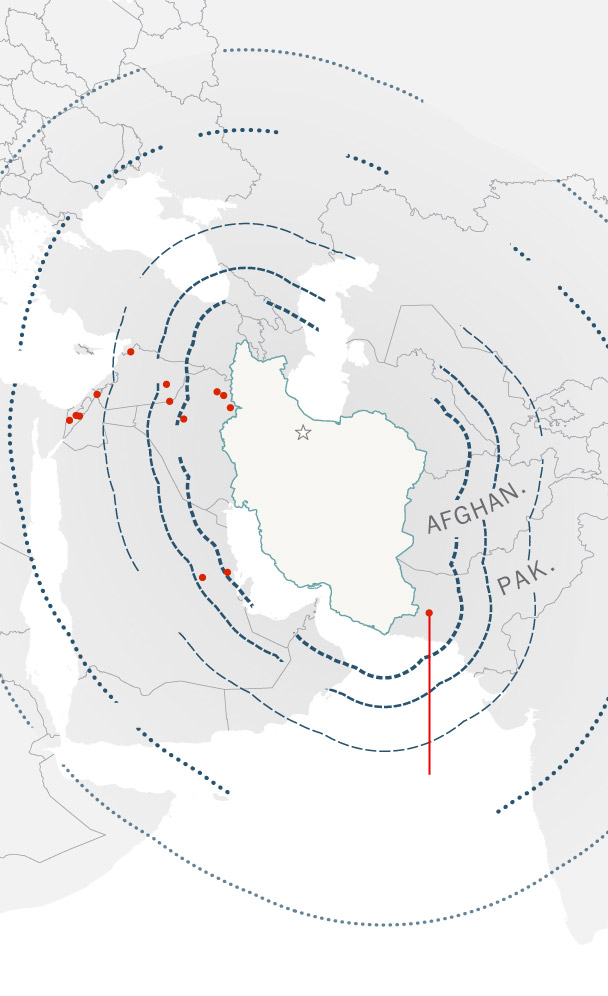
Iranian ballistic
missile ranges
Places of Iranian
missile strikes
since 2017
However the assault on Israel means that a lot of Iran’s munitions are of low high quality. Israel’s army stated 99 p.c of the missiles and drones launched by Iran had been intercepted or didn’t launch.
“We noticed that accuracy and precision are a piece in progress,” stated Behnam Ben Taleblu, a senior fellow on the Basis for Protection of Democracies who has written extensively about Iran’s missile program. “These weapons alone gained’t win a battle for Iran.”
Iranian drones made up the primary wave of the assault. Low-cost, efficient and straightforward to supply, Iranian drones have been utilized in assaults throughout the Center East for years. Iran has additionally provided drones to Russia for its battle in Ukraine, the place they’ve been lethal.
Through the assault on Israel, the slow-moving drones had been most likely deployed to occupy air defenses and permit extra superior munitions to get by means of. All of the drones had been shot down earlier than getting into Israeli airspace, the Israel Protection Forces stated.
Ali Hamie, a Lebanese army analyst, stated Iran had most likely gleaned essential classes about Israel’s aerial defenses. Commentators on Iranian state tv have made comparable factors.
“It could possibly be a testing assault,” Hamie stated, “and the Iranians obtained what they need. Making it previous the air defenses isn’t solely a symbolic victory, however actual victory.”
One of many few missiles to make it by means of the interceptors hit an Israeli air base within the Negev desert. Photographs of the strike had been run on loop on many state-run Iranian broadcasters within the days after the assault. Israel characterised the injury as minor.
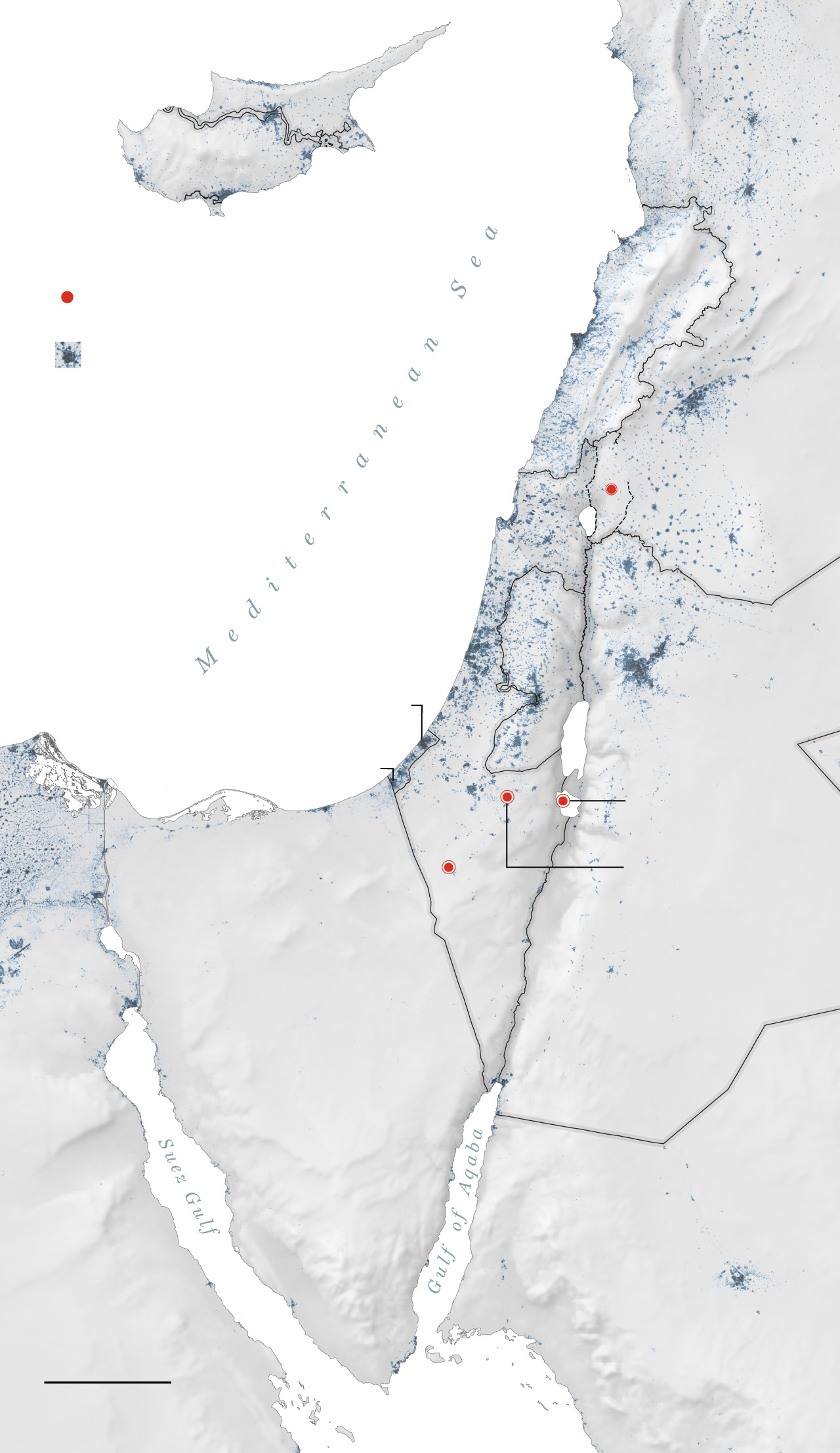
Common location of missile strikes
that reached the bottom.
An emad missile
was discovered right here.
The barrage of
missiles from Iran
included concentrating on
the Nevatim
air base.
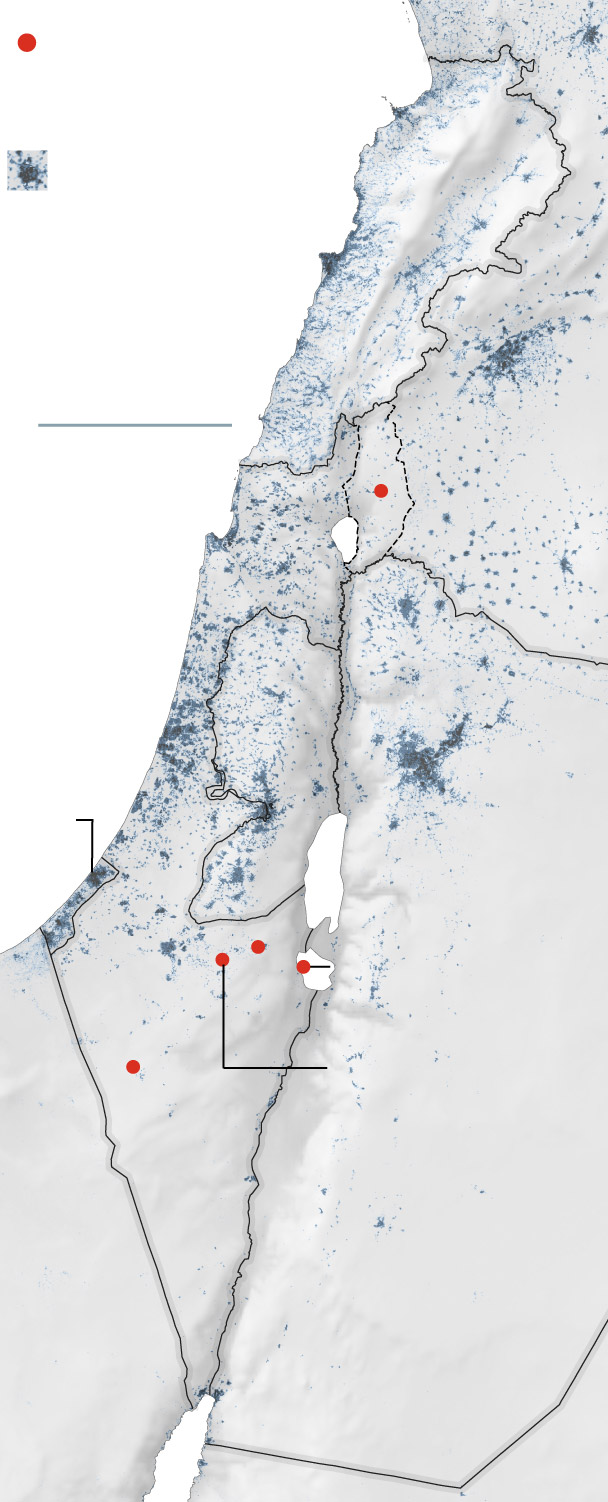
Common location of
missile strikes that
reached the bottom.
An emad missile
was discovered right here.
The barrage of
missiles from Iran
included concentrating on
the Nevatim
air base.
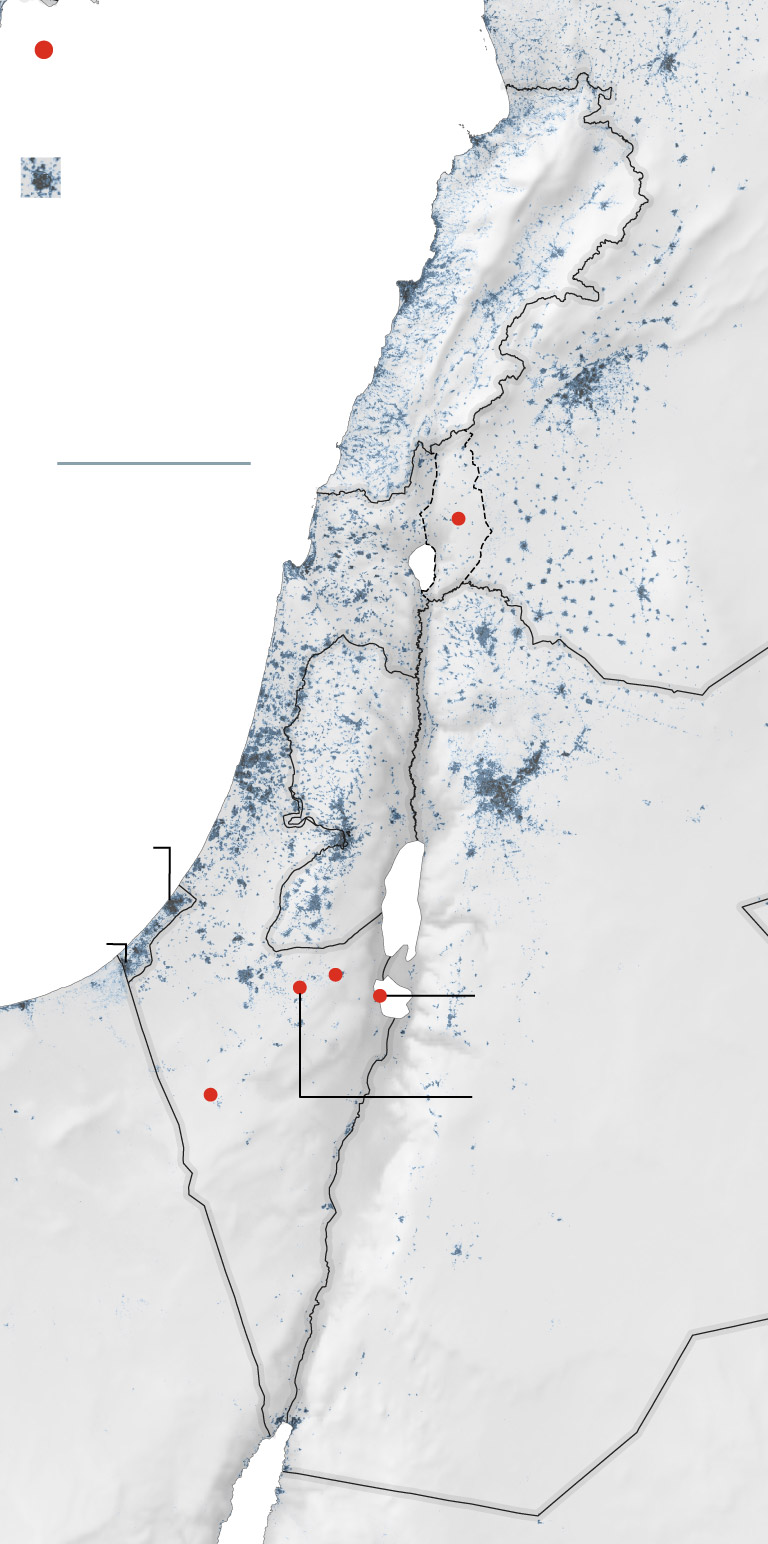
Common location of missile
strikes that reached the
floor.
An emad missile
was discovered right here.
The barrage of
missiles from Iran
included concentrating on
the Nevatim
air base.
Along with analyzing Israel’s air defenses, Tehran will most likely even be learning the issues with its missile programs that reportedly led to failures at launch and in flight, in accordance with Afshon Ostovar, a professor of nationwide safety affairs on the Naval Postgraduate College in California.
“One other assault could possibly be more practical,” he stated. However finally the sort of method demonstrated in Saturday’s assault “isn’t actually sustainable over a long-term battle.”
Even when Iran modified the tempo of assaults and adjusted the munitions used, “they’d nonetheless need to launch various stuff for just some [munitions] to get by means of,” he stated.
Some Iranian officers have advised they’ve held again their most harmful weapons.
“We’re ready to make use of weapons we’ve got by no means used earlier than. We now have plans for each situation,” stated Abolfazl Amoui, a parliamentary nationwide safety spokesman, in an interview with Lebanese broadcaster Mayadeen.
However analysts say it’s unlikely that anybody sort of munition could possibly be a sport changer. Slightly, it’s extra probably Iran would use the identical sorts of munitions in a future assault, however otherwise: giving much less warning, or launching the barrage in live performance with allied militant teams within the area. The nation’s proxy forces, from Lebanon to Iraq to Yemen, performed little position in Saturday’s assault.
As Israel mulls its response, Tehran has warned {that a} counterattack would are available “a matter of seconds.”
“Iran is not going to wait for one more 12 days to reply,” Deputy Overseas Minister Ali Bagheri Kani stated Monday.
Whereas the US and Israel have celebrated the thwarting of Saturday’s assault, analysts are urging humility.
“The variety of munitions it took to repel the assault was huge, pricey and could possibly be tough to duplicate,” stated Tom Karako, the director of the Missile Protection Mission on the Middle for Strategic and Worldwide Research.
“Israel could have gotten fortunate and Iran could have gotten very unfortunate.”
William Neff and Suzan Haidamous contributed to this report.



:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/tl-what-to-take-on-domestic-european-flights-tout-87752c23f9c349dd9f156a9335c9c5db.jpg?w=150&resize=150,150&ssl=1)














:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/tl-what-to-take-on-domestic-european-flights-tout-87752c23f9c349dd9f156a9335c9c5db.jpg?w=768&resize=768,0&ssl=1)



+ There are no comments
Add yours