A model of this submit initially appeared on Tedium, Ernie Smith’s publication, which hunts for the top of the lengthy tail.
Private computing has modified so much previously 4 many years, and one of many greatest adjustments, maybe probably the most unheralded, comes right down to compatibility. As of late, you usually can’t fry a pc by plugging in a joystick that the pc doesn’t assist. Merely put, standardization slowly mounted this. Probably the greatest examples of a bedrock customary is the peripheral element interconnect, or PCI, which happened within the early Nineties and appeared in among the decade’s earliest client machines three many years in the past this yr. To this present day, PCI slots are used to attach community playing cards, sound playing cards, disc controllers, and different peripherals to laptop motherboards through a bus that carries knowledge and management alerts. PCI’s classes steadily formed different requirements, like USB, and in the end made computer systems much less irritating. So how did we get it? By means of a second of canny deception.
Industrial – Intel Inside Pentium Processor (1994)www.youtube.com
Embracing requirements: the computing trade’s reward to itself
Within the Nineteen Eighties, if you used the likes of an Apple II or a Commodore 64 or an MS-DOS machine, you had been basically locked into an ecosystem. Floppy disks typically weren’t suitable. The peripherals didn’t work throughout platforms. In case you needed to promote {hardware} within the Nineteen Eighties, you had been caught constructing a number of variations of the identical gadget.
For instance, the KoalaPad was a standard drawing instrument bought within the early Nineteen Eighties for quite a few platforms, together with the Atari 800, the Apple II, the TRS-80, the Commodore 64, and the IBM PC. It was basically the identical gadget on each platform, and but, KoalaPad’s producer, Koala Applied sciences, needed to make 5 totally different variations of this gadget, with 5 totally different manufacturing processes, 5 totally different connectors, 5 totally different software program packages, and a whole lot of overhead. It was wasteful, made being a {hardware} producer extra pricey, and added to client confusion.
Drawing on a 1983 KoalaPad (Apple IIe)www.youtube.com
This slowly started to alter in round 1982, when the market of IBM PC clones began taking off. It was a cheerful accident—IBM’s determination to make use of a bunch of off-the-shelf parts for its PC by accident turned them right into a de facto customary. Steadily, it turned more durable for computing platforms to change into islands unto themselves. Even when IBM itself tried and didn’t promote the computing world on a bunch of proprietary requirements in its PS/2 line, it didn’t work. The cat was already out of the bag. It was too late.
So how did we find yourself with the requirements that we’ve at the moment, and the PCI growth card customary particularly? PCI wasn’t the one recreation on the town—you can argue, for instance, that if issues performed out in a different way, we’d all be utilizing NuBus or Micro Channel structure. However it was a normal seemingly for the lengthy haul, far past different competing requirements of its period.
Who’s liable for spearheading this customary? Intel. Whereas PCI was a cross-platform know-how, it proved to be an essential technique for the chipmaker to consolidate its energy over the PC market at a time when IBM had taken its foot off the gasoline, selecting to deal with its personal PowerPC structure and narrower performs just like the ThinkPad as an alternative, and was now not shaping the structure of the PC.
The imaginative and prescient of PCI was easy: an interconnect customary that was not meant to be restricted to at least one line of processors or one bus. However don’t mistake standardization for cooperation. PCI was a chess piece—part of a unique recreation than the one PC producers had been enjoying.
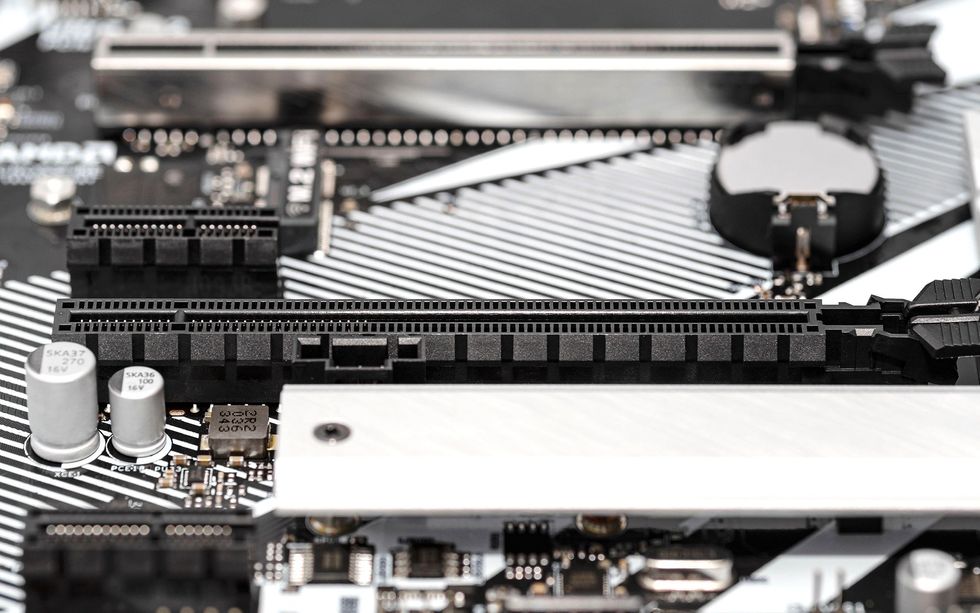 The PCI customary and its derivatives have endured for over three many years. Fashionable computer systems with a GPU typically use a PCIe interconnect. Alamy
The PCI customary and its derivatives have endured for over three many years. Fashionable computer systems with a GPU typically use a PCIe interconnect. Alamy
Within the early Nineties, Intel wanted a win
Within the years earlier than Intel’s Pentium chipset got here out in 1993, there appeared to be some skepticism about whether or not Intel may keep its standing on the forefront of the desktop-computing area.
In lower-end client machines, gamers like Superior Micro Gadgets (AMD) andCyrix had been beginning to shake their weight round. On the excessive finish of the skilled market, workstation-level computing from the likes of Solar Microsystems, Silicon Graphics, and Digital Gear Company urged there wasn’t room for Intel in the long term. And laterally, the corporate immediately discovered itself competing with a triple risk of IBM, Motorola, and Apple, whose PowerPC chip was about to hit the market.
A Bloomberg piece from the interval painted Intel as being boxed in between these varied extremes:
If its rivals preserve gaining, Intel may finally lose floor throughout.
That is no idle risk. Cyrix Corp. and Chips & Applied sciences Inc. have re-created—and improved—Intel’s 386 with out, they are saying, violating copyrights or patents. AMD has no less than briefly received the precise in courtroom to make 386 clones below a licensing deal that Intel canceled in 1985. Previously 12 months, AMD has received 40% of a market that since 1985 has given Intel $2 billion in earnings and a $2.3 billion money hoard. The 486 could endure subsequent. Intel has been chopping its costs quicker than for any new chip in its historical past. And in mid-Could, it chopped 50% extra from one mannequin after Cyrix introduced a chip with some comparable options. Though the common worth of a 486 remains to be 4 occasions that of a 386, analysts say Intel’s earnings could develop lower than 5% this yr, to about $850 million.
Intel’s chips face one other problem, too. Ebbing demand for private computer systems has slowed innovation in superior PCs. This has left a spot on the prime—and most worthwhile—finish of the desktop market that Solar, Hewlett-Packard Co., and different makers of highly effective workstations are working to fill. Because of microprocessors primarily based on a know-how often called RISC, or lowered instruction-set computing, workstations have dazzling graphics and extra oomph—useful for doing complicated duties and transferring knowledge quicker over networks. And a few are as low cost as high-end PCs. So the workstation makers are actually making inroads amongst such PC patrons as inventory merchants, banks, and airways.
This was a deep underestimation of Intel’s market place, it turned out. The corporate was truly well-positioned to form the route of the trade via standardization. They’d a direct say on what appeared on the motherboards of thousands and thousands of computer systems, and that gave them spectacular energy to wield. If Intel didn’t need to assist a given customary, that customary would possible be useless within the water.
How Intel crushed a requirements physique on the way in which to giving us a necessary know-how
The Video Electronics Requirements Affiliation, or VESA, is probably greatest recognized at the moment for its mounting system for laptop screens and itsDisplayPort know-how. However within the early Nineties, it was engaged on a video-focused successor to the Business Commonplace Structure (ISA) inner bus, broadly utilized in IBM PC clones.
A bus, the bodily wiring that lets a CPU speak to inner and exterior peripheral gadgets, is one thing of a bedrock of computing—and within the flawed setting, a bottleneck. The ISA growth card slot, which had change into a de facto customary within the Nineteen Eighties, had given the IBM PC clone market one thing to construct towards throughout its first decade. However by the early Nineties, for high-bandwidth purposes, notably video, it was holding again innovation. It simply wasn’t quick sufficient to maintain up, even after it had been upgraded from with the ability to deal with 8 bits of information directly to 16.
That’s the place the VESA Native Bus (VL-Bus) got here into play. Constructed to work solely with video playing cards, the usual supplied a quicker connection, and will deal with 32 bits of information. It was focused on the Tremendous VGA customary, which supplied larger decision (as much as 1280 x 1024 pixels) and richer colours at a time when Home windows was lastly beginning to take maintain available in the market. To beat the restrictions of the ISA bus, graphics card and motherboard producers began collaborating on proprietary interfaces, creating an array of incompatible graphics buses. The dearth of a constant expertise round Tremendous VGA led to VESA’s formation. The brand new VESA slot, which prolonged the present 16-bit ISA bus with an extra 32-bit video-specific connector, was an try to repair that.
It wasn’t a large leap—extra like a stopgap enchancment on the way in which to higher graphics.
And it seemed like Intel was going to go for the VL-BUS. However there was one downside—Intel truly wasn’t feeling it, and Intel didn’t precisely make that time clear to the businesses supporting the VESA requirements physique till it was too late for them to react.
Intel revealed its hand in an attention-grabbing approach, in keeping with TheSan Francisco Examinertech reporter Gina Smith:
Till now, nearly everybody anticipated VESA’s so-called VL-Bus know-how to be the usual for constructing native bus merchandise. However simply two weeks earlier than VESA was planning to announce what it got here up with, Intel floored the VESA native bus committee by saying it received’t assist the know-how in spite of everything. In a letter despatched to VESA native bus committee officers, Intel acknowledged that supporting VESA’s native bus know-how “was now not in Intel’s greatest curiosity.” And sources say it went on to counsel that VESA and Intel ought to work collectively to attenuate the unfavorable press impression which may come up from the choice.
Good luck, Intel. As a result of now that Intel plans to announce a competing group that features {hardware} heavyweights like IBM, Compaq, NCR and DEC, prospects and traders (and sure, the press) are going to marvel what on the earth is occurring.
Not surprisingly, the individuals who work for VESA are harm, confused and indignant. “It’s a political nightmare. We’re extraordinarily stunned they’re doing this,” mentioned Ron McCabe, chairman for the committee and a product supervisor at VESA member Tseng Labs. “We’ll nonetheless generate income and Intel will nonetheless generate income, however as an alternative of 1 customary, there’ll now be two. And it’s the client who’s going to get harm ultimately.”
However Intel had seen a chance to place its imprint on the computing trade. That chance got here within the type of PCI, a know-how that the agency’s Intel Structure Labs began creating round 1990, two years earlier than the fateful rejection of VESA. Primarily, Intel had been enjoying each side on the requirements entrance.
Why PCI
Why make such a tough shift, screwing over a trusted trade requirements physique out of nowhere? Past wanting to place its mark on the usual, Intel additionally noticed a chance to construct one thing extra future-proof; one thing that would profit not simply graphic playing cards however each growth card within the machine.
As John R. Quinn wrote in PC Journal in 1992:
Intel’s PCI bus specification requires extra work on the a part of peripheral chip-makers, however presents a number of theoretical benefits over the VL-Bus. Within the first place, the specification permits as much as ten peripherals to work on the PCI bus (together with the PCI controller and an non-compulsory expansion-bus controller for ISA, EISA, or MCA). It, too, is proscribed to 33 MHz, however it permits the PCI controller to make use of a 32-bit or a 64-bit knowledge connection to the CPU.
As well as, the PCI specification permits the CPU to run concurrently with bus-mastering peripherals—a mandatory functionality for future multimedia duties. And the Intel strategy permits a full burst mode for reads and writes (Intel’s 486 solely permits bursts on reads).
Primarily, the PCI structure is a CPU-to-local bus bridge with FIFO (first in, first out) buffers. Intel calls it an “intermediate” bus as a result of it’s designed to uncouple the CPU from the growth bus whereas sustaining a 33-MHz 32-bit path to peripheral gadgets. By taking this strategy, the PCI controller makes it attainable to queue writes and reads between the CPU and PCI peripherals. In concept, this may allow producers to make use of a single motherboard design for a number of generations of CPUs. It additionally means extra refined controller logic is important for the PCI interface and peripheral chips.
To place that each one one other approach, VESA got here up with a barely quicker bus customary for the following technology of graphics playing cards, one simply quick sufficient to fulfill the wants of Intel’s latest i486 microprocessor customers. Intel got here up with an interface designed to reshape the following decade of computing, one which it will let its opponents use. This bus would enable individuals to improve their processor throughout generations without having to improve their motherboard. Intel introduced a gun to a knife battle, and it made the entire debate about VL-Bus appear insignificant briefly order.
The end result was that, regardless of how miffed the VESA of us had been, Intel had consolidated energy for itself by creating an open customary that will finally win the following technology of computer systems. Positive, Intel let different firms use the PCI customary, even firms like Apple that weren’t instantly doing enterprise with Intel on the CPU facet. However Intel, by pushing forth PCI, immediately made itself related to the complete subsequent technology of the computing trade in a approach that ensured it will have a second foothold in {hardware}. The “Intel Inside” advertising label was not restricted to the processors, because it turned out.
The affect of Intel’s introduction of PCI remains to be felt: Thirty-two years later, and three many years after PCI turned a significant client customary, we’re nonetheless utilizing PCI derivatives in fashionable computing gadgets.
PCI and different requirements
Taking a look at PCI, and its successor PCI categorical, much less as ways in which we join the peripherals we use with our computer systems, and extra as a approach for Intel to take care of its dominance over the PC trade, highlights one thing fascinating about standardization.
It seems that maybe Intel’s best funding in computing within the Nineties was not the Pentium chipset, however its funding in Intel Structure Labs, which quietly made the complete computing trade higher by engaged on the issues that pissed off customers and producers alike.
Primarily, as IBM had begun to take its eye off the large clone promote it unwittingly constructed throughout this era, Intel used standardization to fill the ability void. It labored fairly nicely, and made the corporate integral to laptop {hardware} past the CPU. Actually, gadgets you utilize day by day—that Intel performed zero half in creating—have benefited drastically from the corporate’s requirements work. In case you’ve ever used a tool with a USB or Bluetooth connection, you may thank Intel for that.
Craig Kinnie, the director of Intel Structure Labs within the Nineties, mentioned it greatest in 1995, upon coming to an settlement with Microsoft on a 3D graphics structure for the PC platform. “What’s essential to us is we transfer in the identical route,” he mentioned. “We’re engaged on convergent paths now.”
That was about collaborating with Microsoft. However actually, it has been Intel’s modus operandi for many years—what’s good for the know-how area is nice for Intel. Improvements developed or invented by Intel—like Thunderbolt, Ultrabooks, and Subsequent Unit Computer systems (NUCs)—have achieved a lot to form the way in which we purchase and use computer systems.
For all of the speak of Moore’s Legislation as a driving issue behind Intel’s success, the true story could be its sheer cat-herding capabilities. The corporate that builds the requirements builds the trade. At the same time as Intel faces rising competitors from alliterative processing gamers like ARM, Apple, and AMD, so long as it doesn’t lose sight of the roles requirements performed in its success, it’d simply maintain on a couple of years longer.
Satirically, Intel’s standards-driving successful streak, now greater than three many years previous, might need all began the day it determined to stroll out on a requirements physique.
From Your Website Articles
Associated Articles Across the Internet





















+ There are no comments
Add yours